Understanding CopyLeaks
CopyLeaks is a content analysis tool designed to scrutinize text for indications of plagiarism and potential copyright infringements. Its primary goal is to ensure the authenticity and originality of written content in various digital contexts, such as documents, web pages, and academic papers.
AI Content Detection Process: Key Steps
- Sign In: Begin by logging into the tool’s platform.
- Input Text: Provide the tool with the text you want to analyze.
- Text Analysis: Advanced algorithms and machine learning examine the content.
- User Review: Users assess results and take necessary actions.
- Repeatable Process: Allows for ongoing content monitoring.
Review Process
In our comprehensive evaluation of CopyLeaks, we followed a structured testing methodology to gauge its effectiveness in detecting both human-written and AI-generated content:
- Phase 1 – Initial Assessment: We started with the basics by giving CopyLeaks 10 human-written pieces and 10 AI-generated ones to see how well it could tell the difference between them.
- Phase 2 – Precision and Reliability Assessment: In this phase, we dissected specific sections of a human-written blog and an AI-generated piece to gauge CopyLeaks’ precision. We subjected entire human-written blogs and AI-generated texts to assess the overall reliability of longer pieces.
- Phase 3 – Deception Exploration: Lastly, in the final phase, we played around with strategies and tricks to see if we could make AI-generated content appear as if it were written by a human. This gave us insights into CopyLeaks’ strengths and weaknesses.
By implementing this rigorous testing process, we aimed to provide you with an informed perspective on CopyLeaks’ performance and its potential susceptibility to content manipulation.
PHASE 1 – Initial Assessment:
To begin, we submitted a total of 20 text samples, comprising 10 human-written pieces and 10 AI-generated articles, to CopyLeaks for analysis. The primary objective was to gauge the tool’s initial aptitude in distinguishing between content crafted by humans and content generated by artificial intelligence.
By subjecting CopyLeaks to this initial test, we aimed to gain insights into its proficiency in content differentiation, setting the stage for subsequent phases of our assessment. This phase’s outcomes laid the groundwork for a deeper understanding of CopyLeaks’ capabilities and its performance in distinguishing between human and AI-generated content.
AI Generated Content
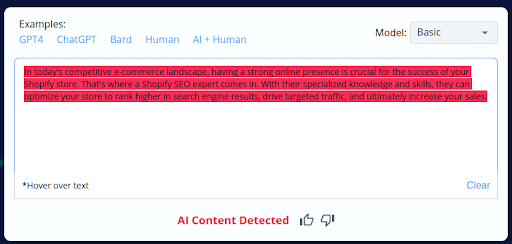
1. 
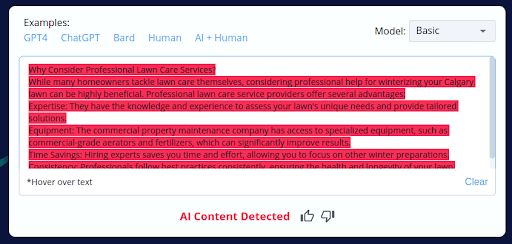
2. 
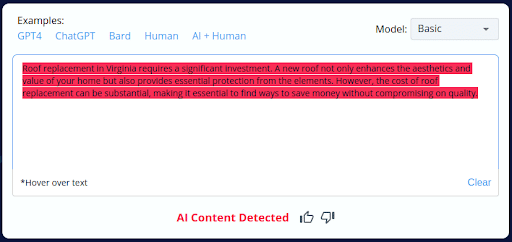
3. 
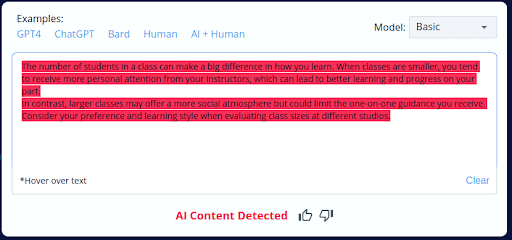
4. 
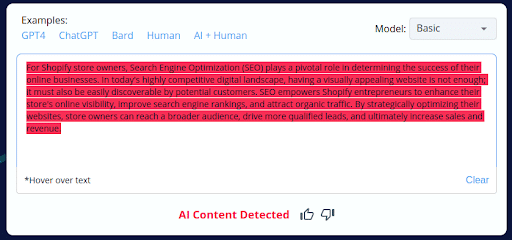
5. 
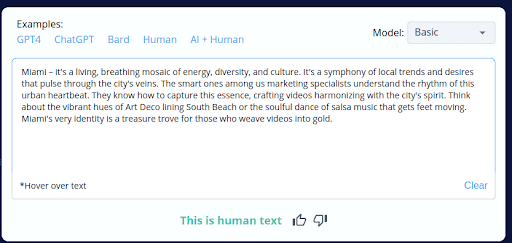
6. 
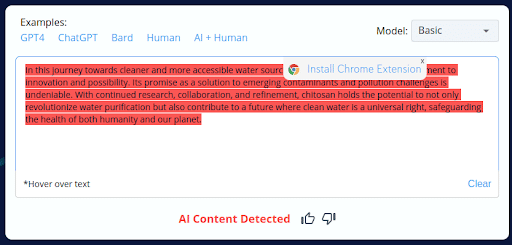
7. 
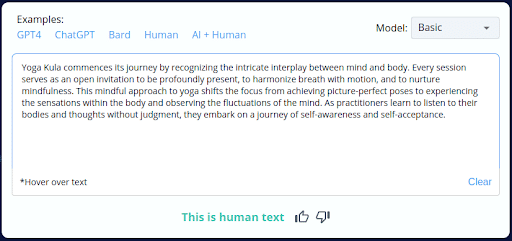
8. 
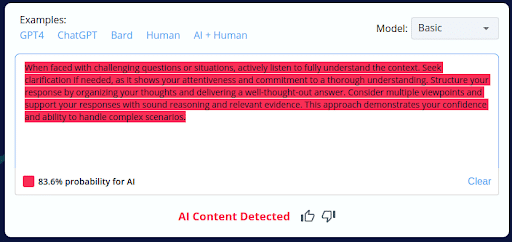
9. 
10. ![]()
- CopyLeaks inaccurately categorized 2 of the 10 AI-generated content pieces as human-written.
- The tool’s inability to consistently distinguish between AI-generated and human-crafted content raises concerns about its accuracy.
- Users should exercise caution and perform manual reviews when using CopyLeaks, especially with AI-generated content.
Human Written Content
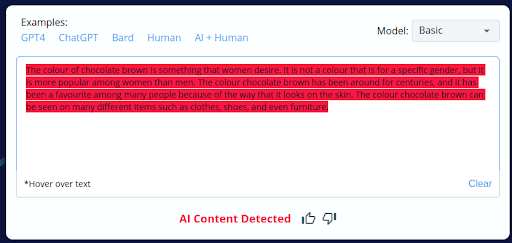
1.
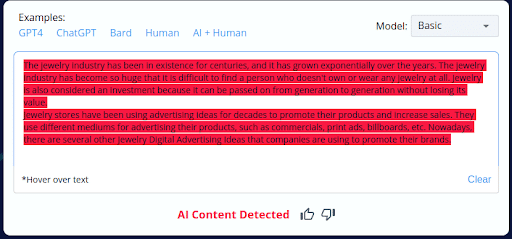
2.
3. 
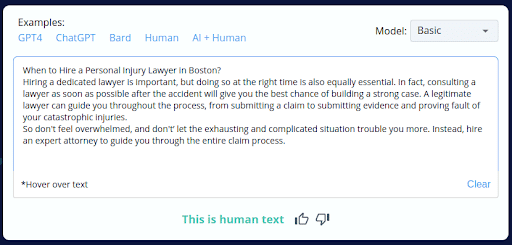
4.
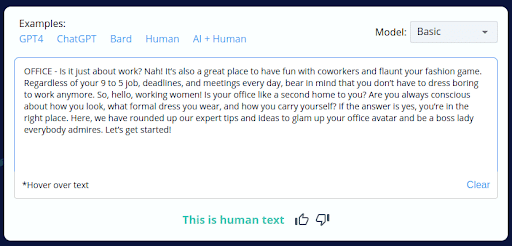
5. 
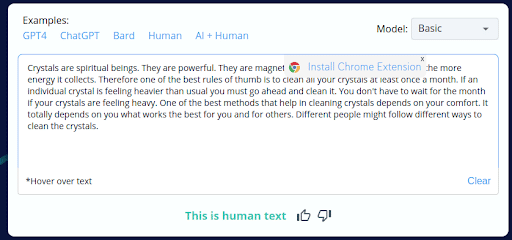
6. 
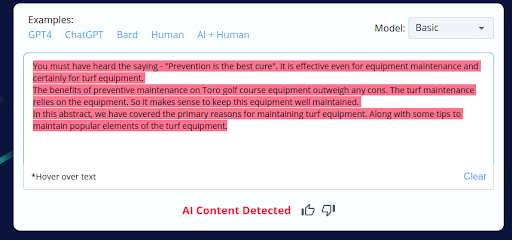
7.
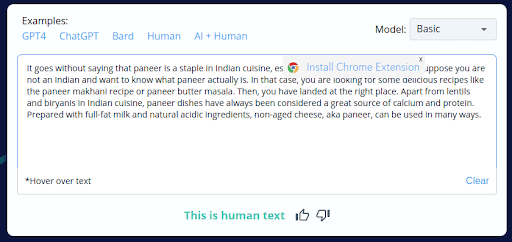
8.
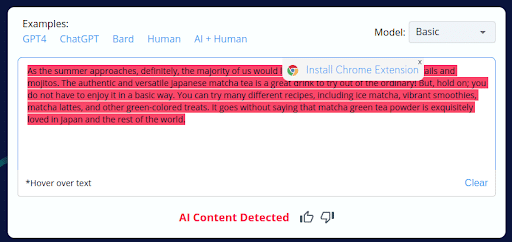
9.
10.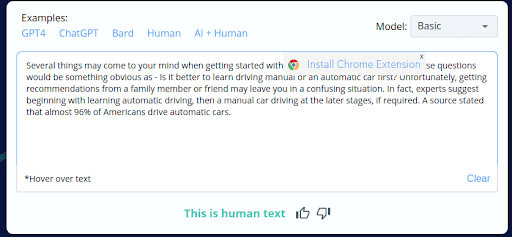
- CopyLeaks’ incorrect labeling of 4 out of 10 human-written content as AI-generated reveals a substantial flaw in its accuracy.
- This unreliability can be concerning for users who depend on CopyLeaks for content analysis, potentially leading to incorrect conclusions and actions.
- This discovery underscores the necessity of manual review and human oversight when utilizing CopyLeaks to ensure content authenticity.
Result of Phase 1 – Initial Assessment:
In our initial phase of testing, we uncovered concerning inaccuracies in CopyLeaks’ performance, raising questions about its reliability:
CopyLeaks demonstrated a concerning overall misclassification rate of 30% (6 out of 20), further highlighting its unreliability in distinguishing between AI-generated and human-written content.
These findings underscore CopyLeaks’ vulnerability to misidentifying the nature of content, with a substantial number of misclassifications in both categories. Such discrepancies cast doubt on the tool’s effectiveness and suggest the need for cautious interpretation of its results, emphasizing the importance of supplementary manual review to ensure accurate content analysis.
PHASE 2 – Precision and Reliability Assessment:
In this phase, we wanted to see how accurately CopyLeaks could spot differences in text. We first picked small parts from a regular human-written blog and an AI-generated piece.
Next, we tested CopyLeaks on the complete human-written blogs and AI-generated texts.
This combined phase helped us understand how precise CopyLeaks is in finding tiny differences in text, and also how dependable it is when dealing with longer documents.
It’s important because real-world documents come in all sizes and complexities. These results gave us a more complete picture of how well CopyLeaks performs in different situations.
AI Generated Content
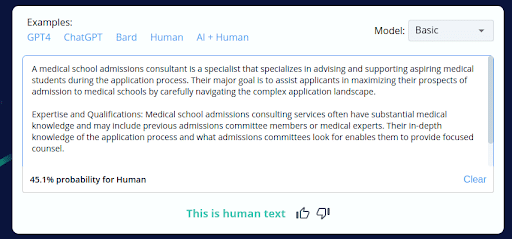
1.

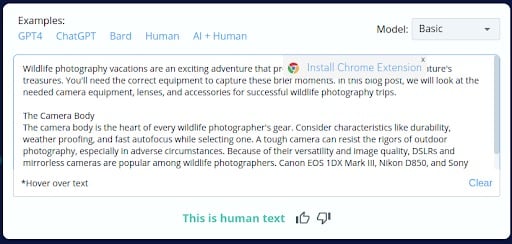
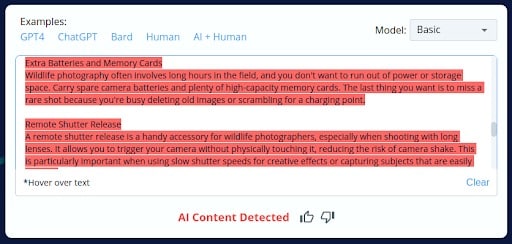
2.
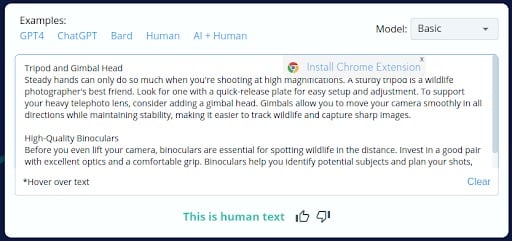
Human Written Content
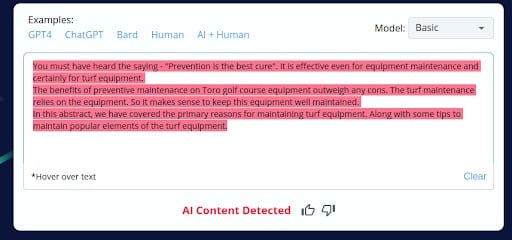
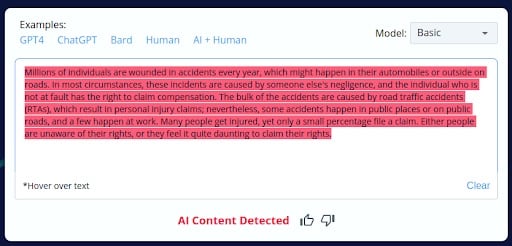
1.
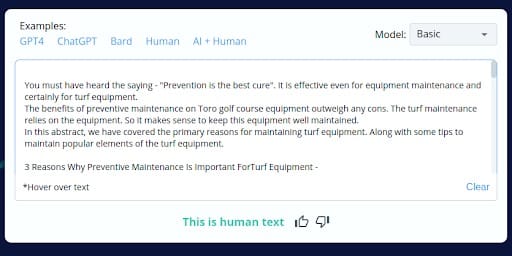
2. 
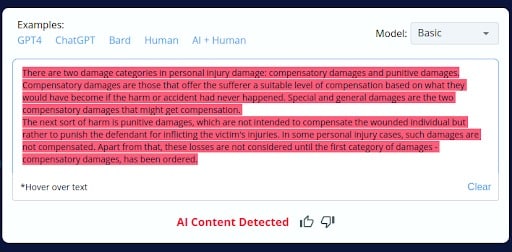
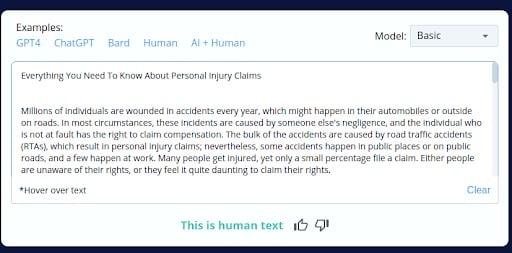
Results of Phase 2 – Precision and Reliability Assessment:
During this phase of testing, we encountered noteworthy inconsistencies in CopyLeaks’ performance, which brought its reliability into question:
- AI Content Misclassification: CopyLeaks inaccurately identified parts of AI-generated content as human-generated but then incorrectly classified the entire AI-generated blog as AI content.
- Human Content Misclassification: Similarly, parts of human-written content were wrongly recognized as AI-generated, but the whole human-written blog was subsequently labeled as human-generated.
These results indicate a significant inconsistency in CopyLeaks’ ability to classify content, both in smaller sections and in its entirety. The tool’s inability to provide uniform results within the same document highlights its unreliability, potentially leading to misleading conclusions and actions when analyzing content for plagiarism or copyright issues.
These findings underscore the importance of exercising caution and employing supplementary manual review when relying on CopyLeaks for content assessment, particularly in situations where content spans various sections and lengths.
Phase 3 – Deception Exploration:
In the final phase of our CopyLeaks evaluation, we embarked on a critical exploration aimed at uncovering the tool’s vulnerabilities, strengths, and weaknesses when confronted with deceptive tactics to pass AI-generated content as human-generated.
This phase provided crucial insights into CopyLeaks’ adaptability and its susceptibility to manipulation.
We intentionally sought to blur the lines between AI-generated and human-crafted content by employing various strategies.
It serves as a reminder of the tool’s potential susceptibility to sophisticated manipulation and calls for vigilance and supplementary manual review when assessing content authenticity.
QuillBot
QuillBot is a popular rephrasing tool known for its ability to rewrite text while preserving its meaning.
In our evaluation, we aimed to test CopyLeaks’ accuracy in distinguishing between AI-generated and human-written content when the QuillBot rephraser was used to modify text.
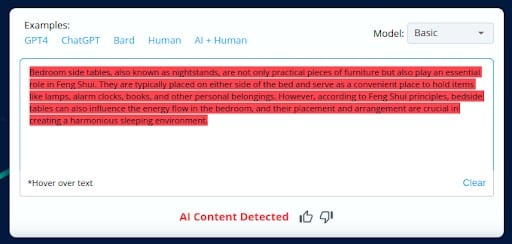
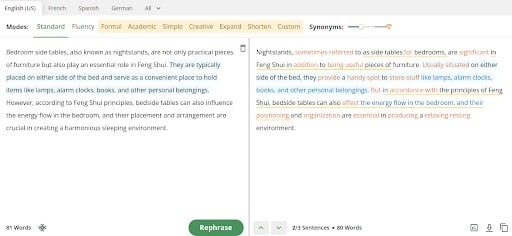
CopyLeaks unexpectedly categorized text that had undergone QuillBot rephrasing as human-generated, despite its origin as AI-generated content.
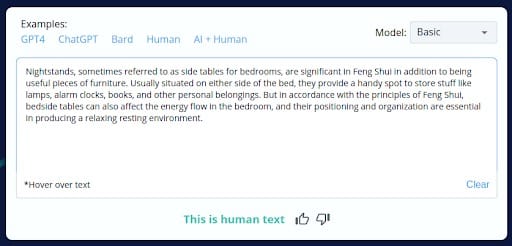
This result highlights a potential vulnerability in CopyLeaks’ detection capabilities when dealing with rephrased text, as it can misclassify AI-generated content as human-generated, potentially leading to misjudgments.
Grammatical Errors
We intentionally introduced grammatical errors into AI-generated text, including the removal of commas, addition of extra spaces, and dashes at the end of paragraphs.
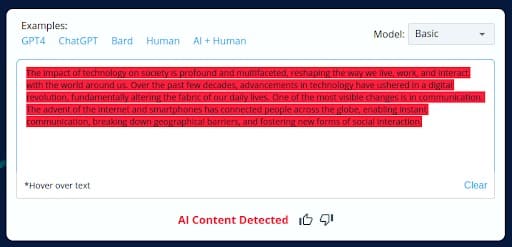
CopyLeaks misclassified this intentionally flawed AI-generated content as human-generated, indicating a significant oversight in its analysis.
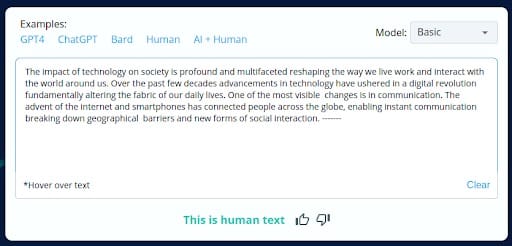
The findings highlight the ongoing challenges in the dynamic landscape of AI-generated content and the need for continuous tool development to maintain accuracy.
AItoHumanConvertor Tool
In our assessment, we sought to test CopyLeaks’ accuracy in distinguishing AI-generated content from human-generated content when aitohumanconverter.com was employed without making any modifications to the text.
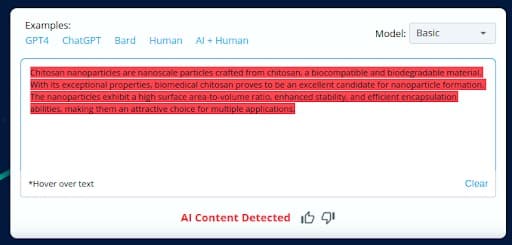
AItoHumanConvertor is a platform known for its ability to transform AI-generated text into human-like content while keeping the text unchanged.
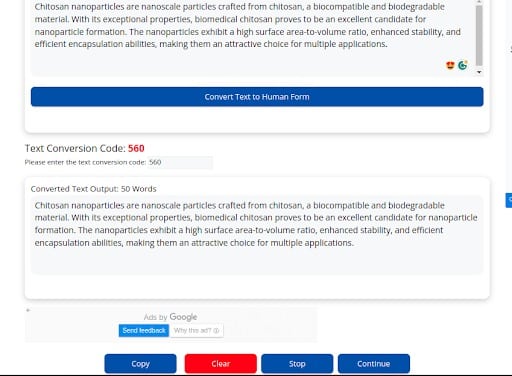
CopyLeaks classified the content transformed by AItoHumanConvertor Tool as human-generated, despite the fact that no changes were made to the original AI-generated text.
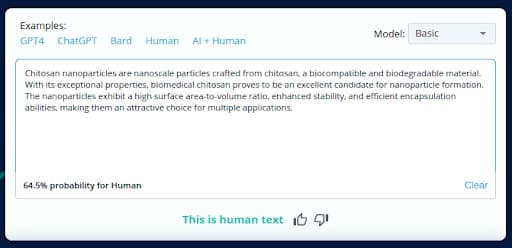
It underscores the challenge of maintaining content integrity and accurate identification in an era where AI can seamlessly mimic human writing styles.
What’s New in CopyLeaks for 2025?
As per the latest Release Notes from CopyLeaks, this is what’s new:
In November 2024, Copyleaks introduced Version 7.1, which:
- Improved AI detection capabilities compared to Version 6.1
- Enhanced AI-to-human paraphraser detections
- Introduced faster and more efficient AI detection
Now, CopyLeaks is claiming that its AI detector is highly accurate with just a 0.2% false positive rate. But is this really the case? Let’s find out.
| NOTE: We also analyzed these results with ZeroGPT for good measure. |
Quick Summary for CopyLeaks Accuracy Test (2025)
|
Review Process 2.0 (2025)
In our comprehensive evaluation of CopyLeaks for 2025, we once again followed a structured testing methodology to gauge its effectiveness in detecting both human-written and AI-generated content.
We split it into three assessments with different testing parameters, where each segment tackled a different use case scenario.
Assessment 1 – Paraphrasing Bot Assessment
100% AI-generated content was paraphrased using AI-to-human tools to see how well it could detect the difference.
Assessment 2 – Precision for Human-edited Sections
In this phase, we edited specific sections of AI-generated texts manually to assess the specialized accuracy of CopyLeaks.
Assessment 3 – Deception Exploration
Unlike our previous test, where we tried to trick the AI model, here we asked CopyLeaks to check 100% human-written content.
By implementing this rigorous testing process, we aimed to provide you with an informed perspective on CopyLeaks’ performance and its potential susceptibility to content manipulation.
Assessment 1: Paraphrased AI Content
Since 2023, not just AI detectors but AI-to-human bots have also evolved drastically. This is why we wanted to check if the latest version of CopyLeaks can detect paraphrased content.
We used Quillbot and StealthWriter.
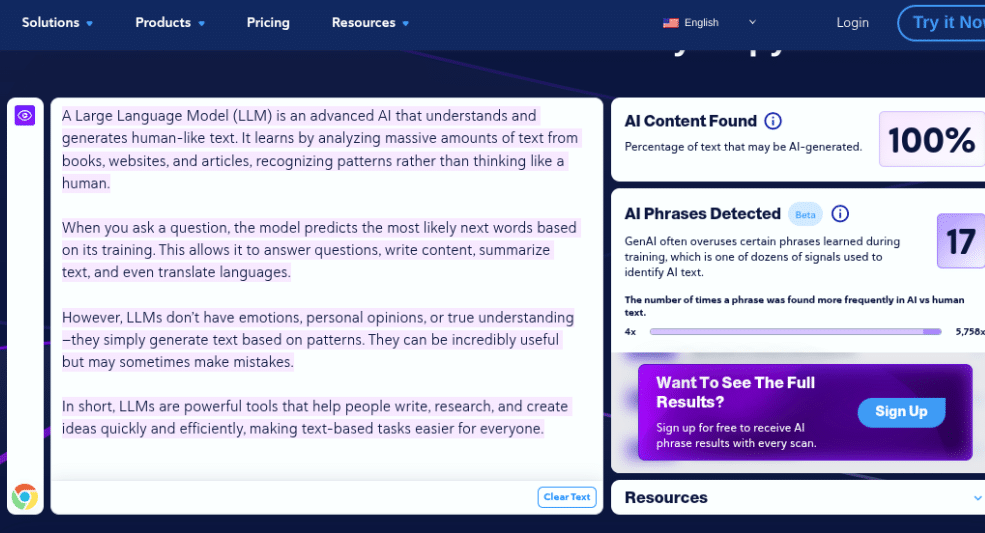
We checked the content without paraphrasing first. As expected, CopyLeaks classified the text as AI content.
Since Quillbot demanded a premium to convert AI-generated content into human-written text, we skipped it and asked ChatGPT to keep the content under 125 words. Why? Most users rely on the free plans.
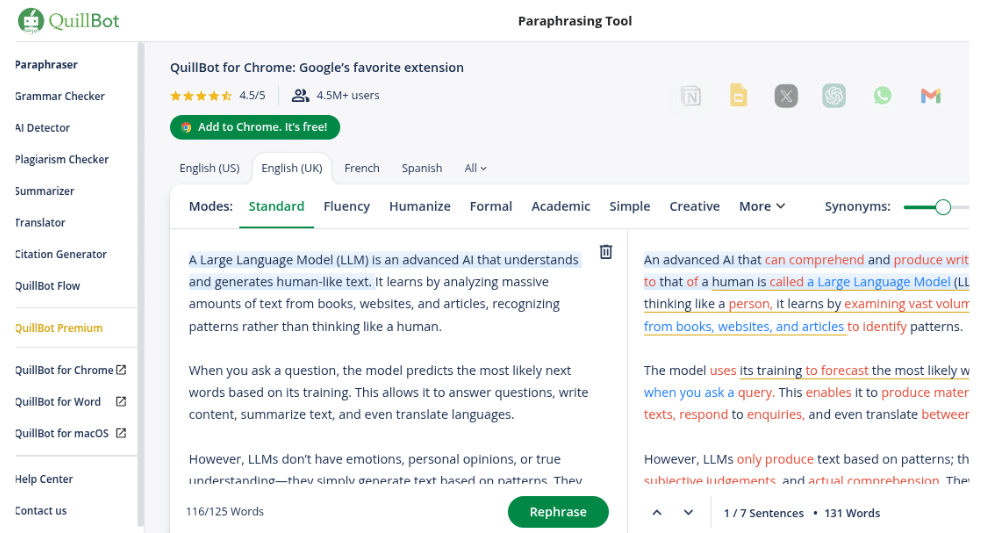
Assessment 1.1 QuillBot
We paraphrased the content with QuillBot, one of the trending AI humanizer in 2025.
Assessment 1.1 QuillBot Results – Pass
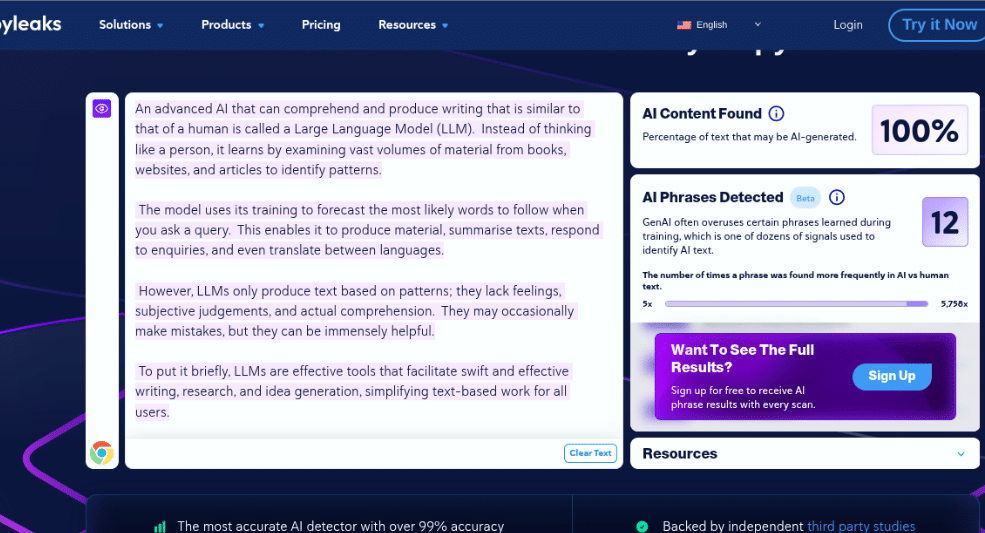
As expected, CopyLeaks can easily detect AI content that is paraphrased by QuillBot humanizer bots. It passed the test with flying colors (100% detection rate).
Assessment 1.1 StealthWriter
Next, we used StealthWriter, Ninja 3.2 to be specific, one of the most popular and functional AI-to-human text converters.

Assessment 1.1 StealthWriter Results – Pass
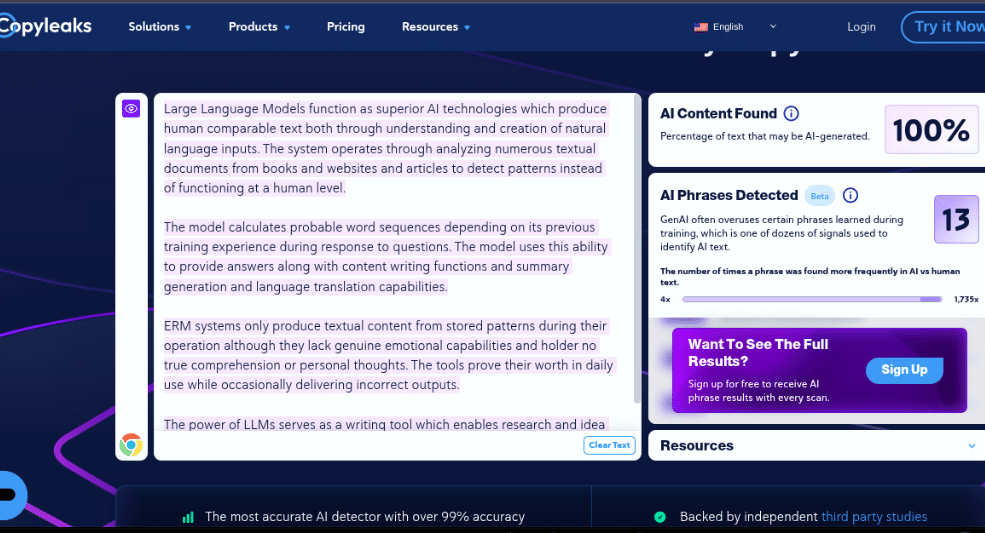
So far, so good. It seems the latest version of CopyLeaks is more accurate in 2025. But is CopyLeaks reliable and consistent?
ZeroGPT – Needs Massive Improvements
Before answering that question, we wanted to check if other AI detection models are on par with CopyLeaks. For this, we used ZeroGPT. However, it misclassified AI-generated content as human-generated content (0% detection rate), paraphrased by QuillBot and StealthWriter.
QuillBot Results
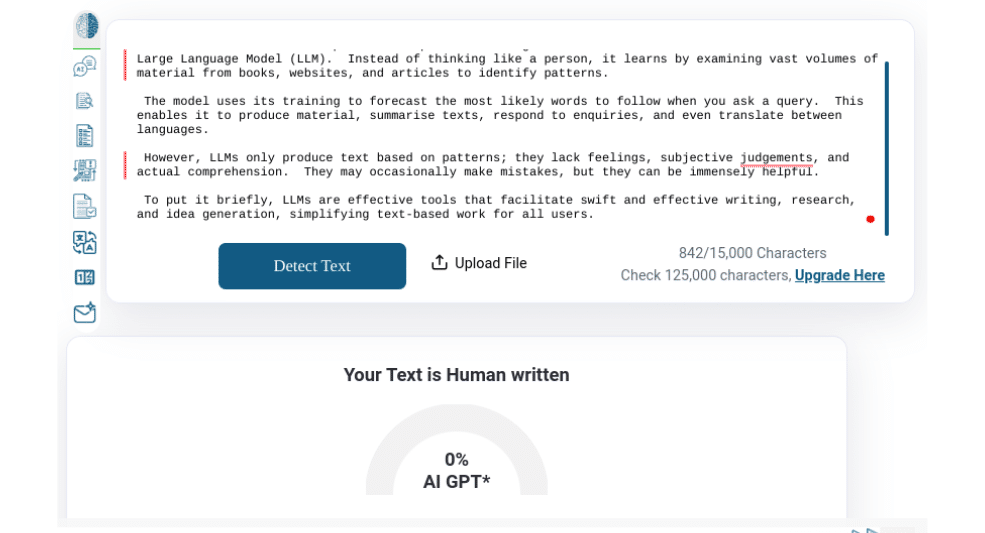
StealthWriter Results
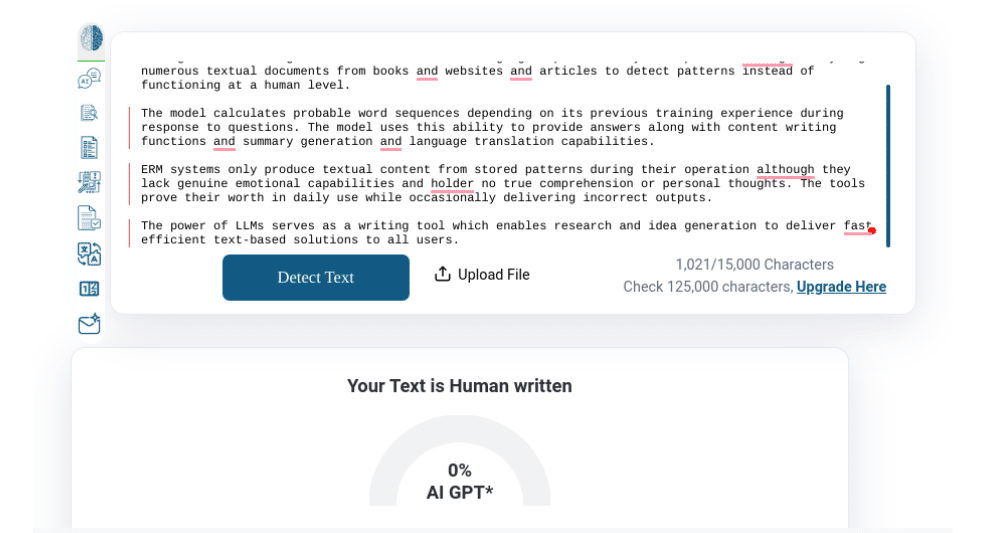
Assessment 1.2 QuillBot – Pass
For this assessment, instead of going technical, we see how CopyLeaks checks for definition-style content. First up was QuillBot, and CopyLeaks nailed this one.
Assessment 1.2 StealthWriter – Fail
Here’s a first of this test. StealthWriter easily tricked CopyLeaks to the point that the paraphrased AI text was labelled as 100% human-written.
Assessment 1.3 QuillBot – Fail
In a surprising turn of events, QuillBot also managed to trick CopyLeaks’ AI model into misclassifying AI content as human. Now, we’re not sure about CopyLeaks’ accuracy.
Assessment 1.3 StealthWriter – Pass
For this assessment, CopyLeaks classified AI content successfully.
Assessment 1.4 QuillBot – Pass
But what about professional LinkedIn posts? It easily detected AI text.
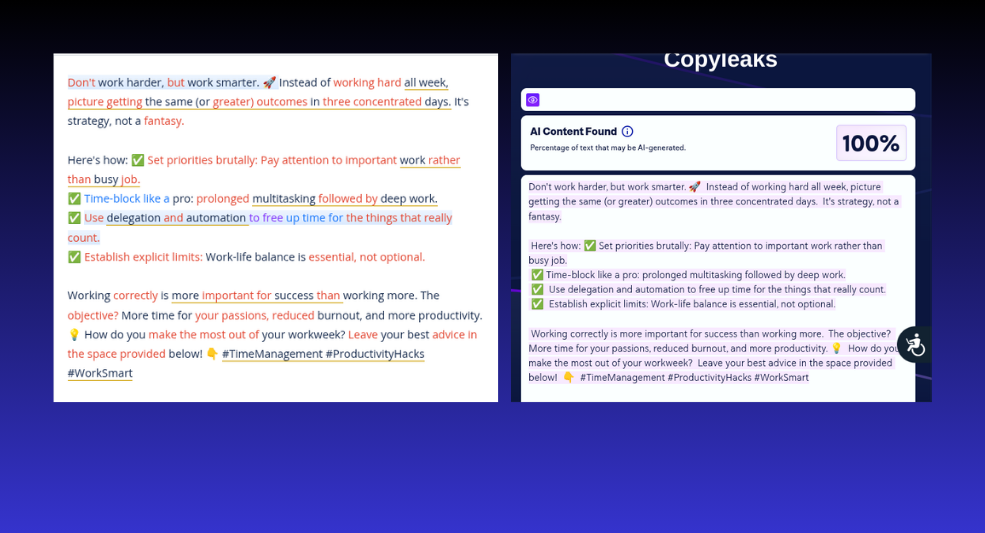
Assessment 1.4 StealthWriter – Pass
Once again, CopyLeaks easily detected AI-generated content.
| NOTE: StealthWriter doesn’t humanize text if it contains markup (<) or emojis. |
Assessment 1.5 QuillBot – Fail
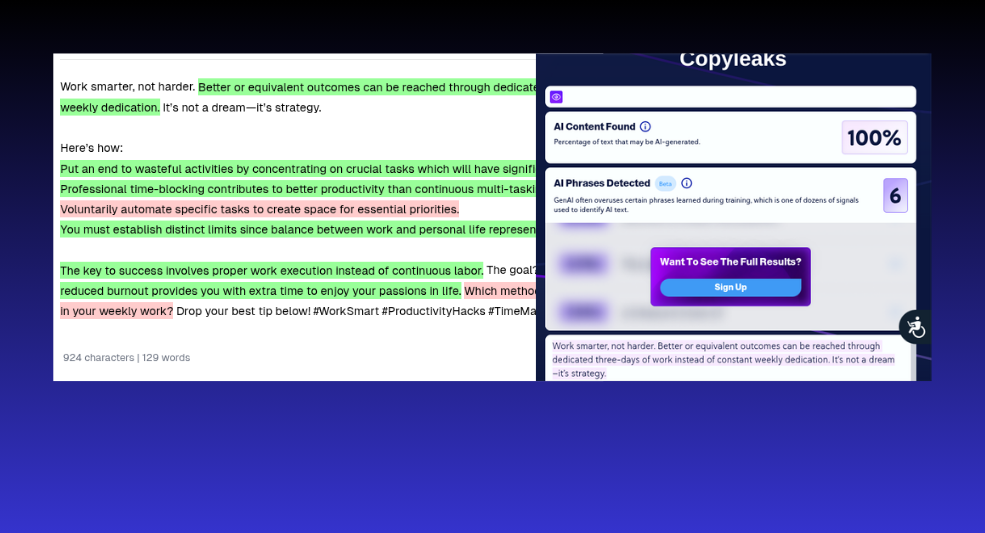
This specific test was to see how CopyLeaks would tackle blogs, and it failed miserably.

Assessment 1.5 StealthWriter – Fail
Once again, CopyLeaks falsely classified AI-generated blogs as human.

Assessment 1 Overall Results
Out of 10 AI paraphrased texts, CopyLeaks detected six of them accurately while it missclassified 4 of them.
CopyLeaks Accuracy Rate for AI Paraphrased Content: 60%
Assessment 2: AI-Generated Content Mixed with Human Input
Now, we’ve established that CopyLeaks can somewhat detect AI-generated content, even paraphrased by humanizer bots. However, what if we introduced human edits to the AI-generated content?
Assessment 2.1
For this, we used the same AI-generated content; however, we asked one of our content specialists to edit it to trick CopyLeaks’ AI detection.

Assessment 2.1 Results – Pass
Once again, CopyLeaks proved itself capable of detecting AI-generated content that is human-edited.
But the interesting thing is that it missclassified the entire content as AI-generated when clearly at least 50% of the content was edited by a human.
This can be particularly infuriating for content creators leveraging AI tools to generate ideas or blueprints.
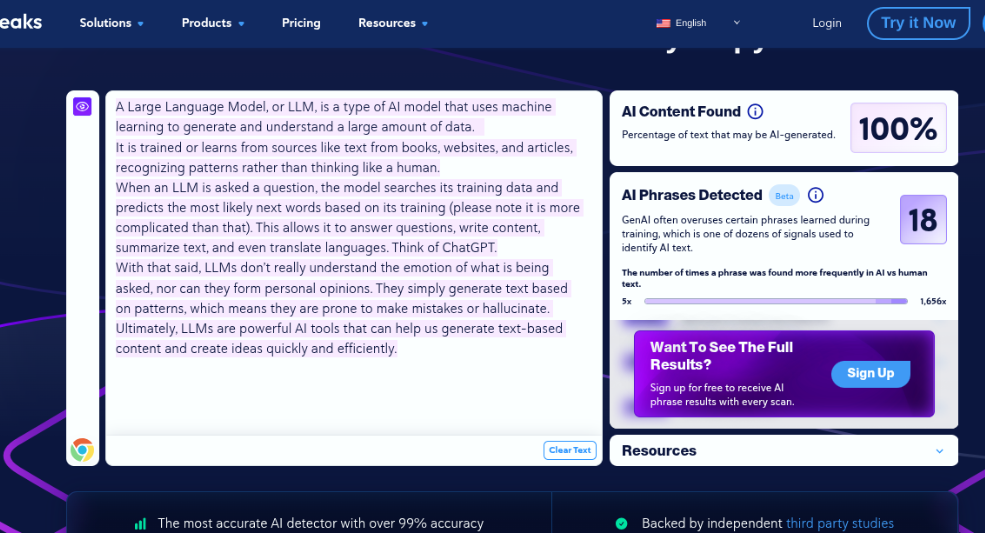
Assessment 2.2
Let’s give CopyLeaks the benefit of the doubt. Maybe the structure of the content was too AI-like, or perhaps it was a little too complex. We tried again with a simpler query.
Interestingly, CopyLeaks detected 96.6% AI-generated content in this one. However, it was entirely generated by ChatGPT.
We made appropriate edits.

Assessment 2.2 Results – Fail
Now, once again, CopyLeaks left us scratching our heads. Unedited content was deemed “more” human than human-edited content. We’re starting to wonder if CopyLeaks is legit for AI detection.
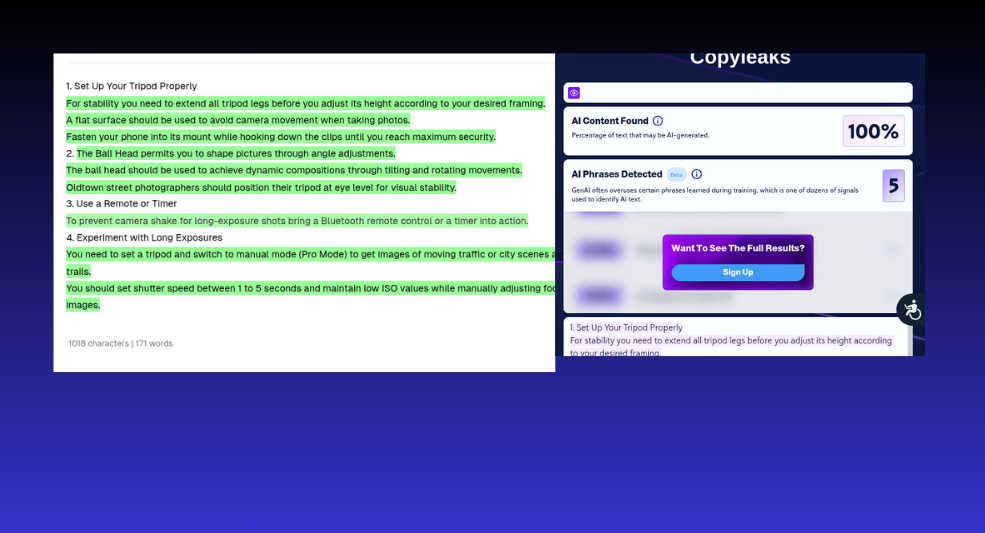
Assessment 2.3
For this one, we asked ChatGPT to “Quickly share how to use a mobile tripod for City photography”.

Assessment 2.3 Results – Fail
Once again, CopyLeaks’ AI checker seemed to completely ignore human addition to the content and labeled everything as AI-generated content.
Assessment 2 Overall Results
Out of 3 human-edited texts, CopyLeaks only detected one of them accurately and gave false positives for the other two.
CopyLeaks Accuracy Rate for Human-edited Content: 33.3%
| NOTE: We were confident that we’d get the AI Content Found message; however, we wanted to check just how much it can separate AI from human content. |
Assessment 3: 100% Human-written Content
So far, the case for CopyLeaks isn’t looking too strong. But it can surely differentiate completely human-written content from AI, right? Let’s find out.
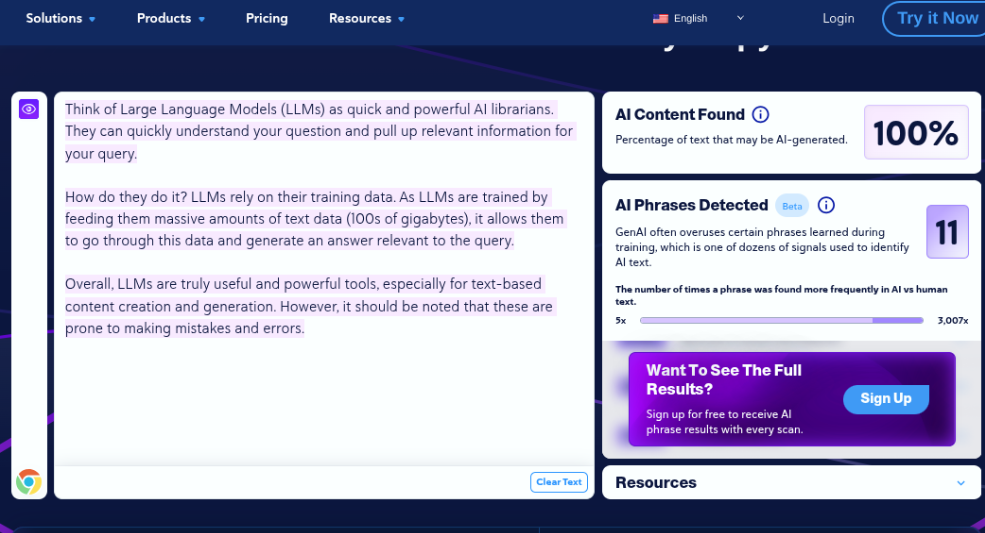
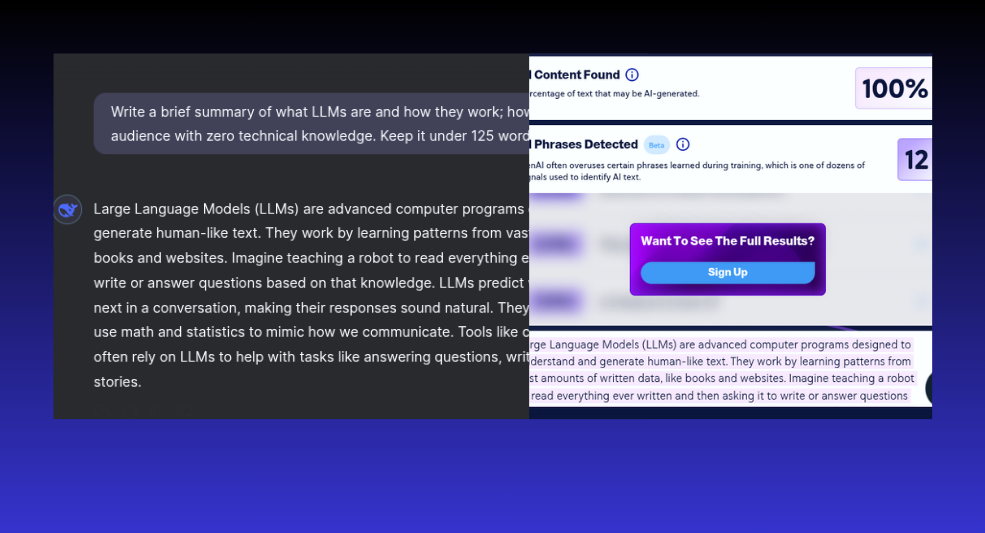
Assessment 3.1
Here, we decided to continue with the LLM explanation; however, a human wrote it from scratch.

Assessment 3.1 Results – Fail
CopyLeaks, what the heck? To all of our surprise, this 100% human-generated content was deemed AI. Perhaps CopyLeaks’ false positive still exists in 2025.
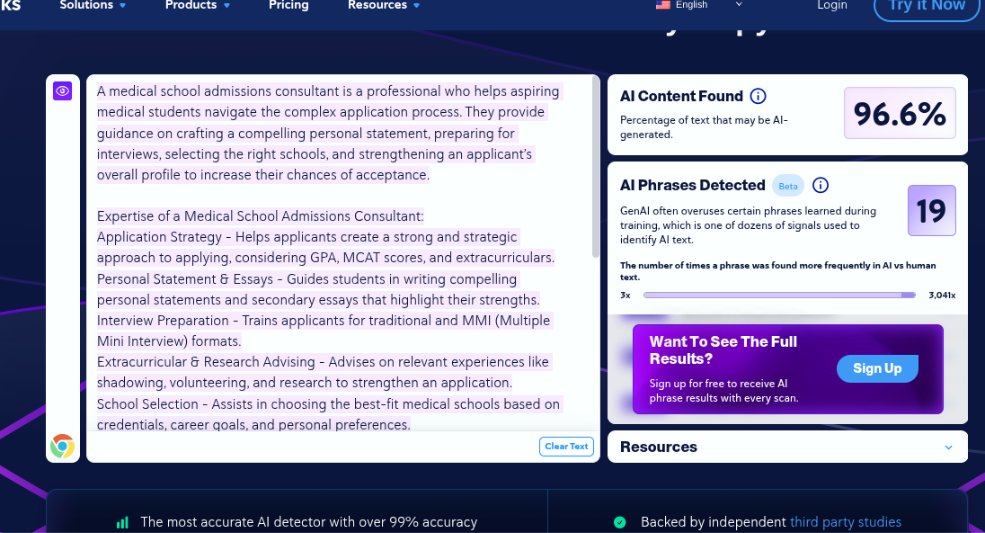
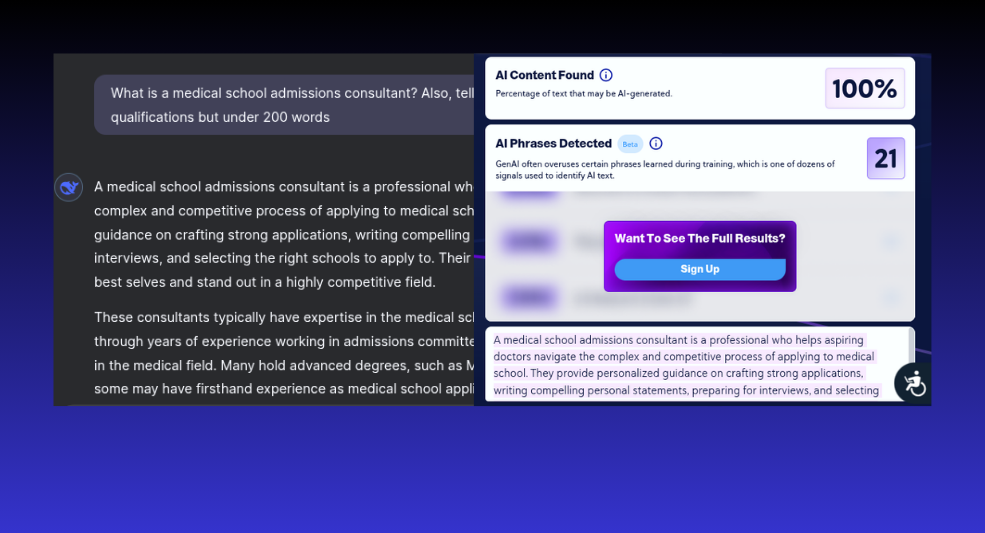
Assessment 3.2
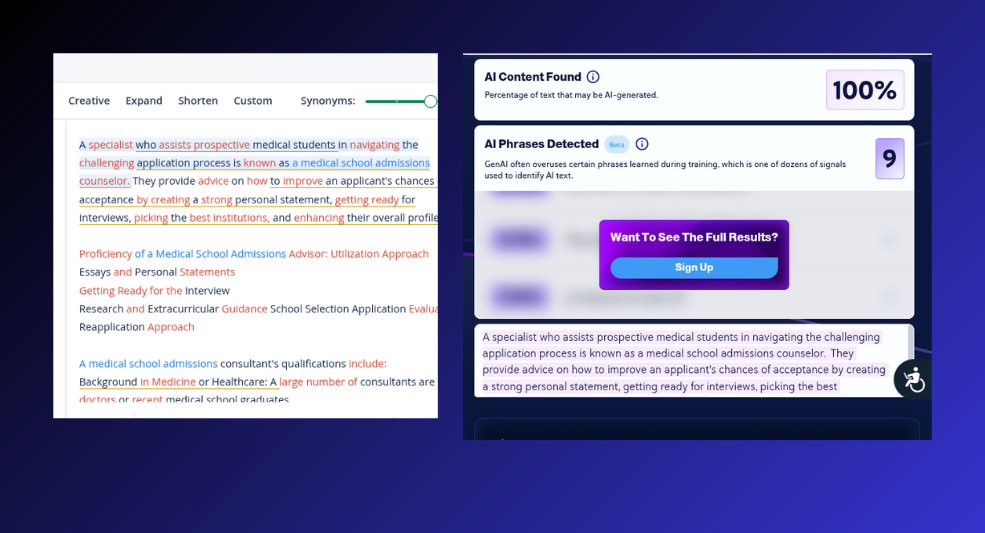
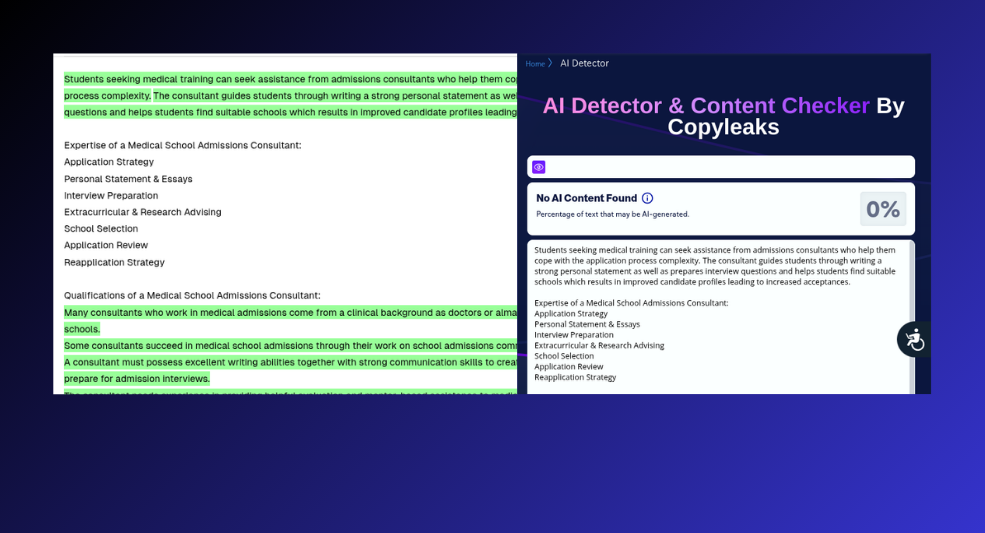
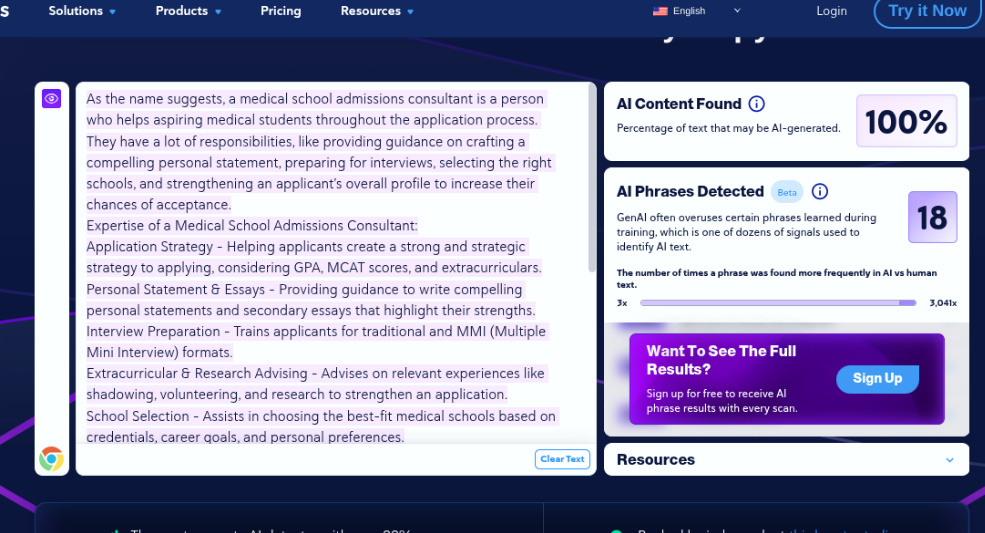
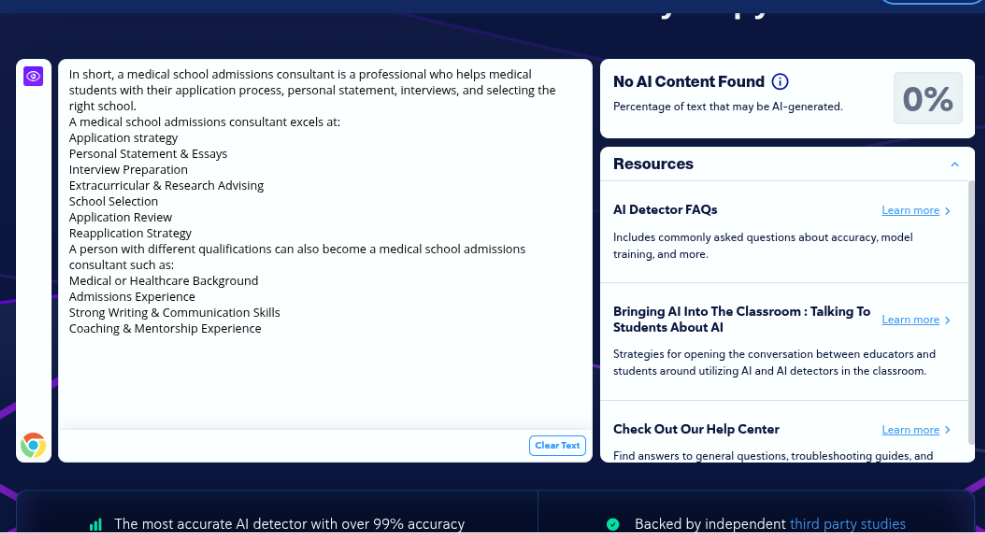
For the second test, we decided to write something about a medical school admissions consultant.

Assessment 3.2 Results – Pass
Fortunately (for CopyLeaks), it detected this content as human.
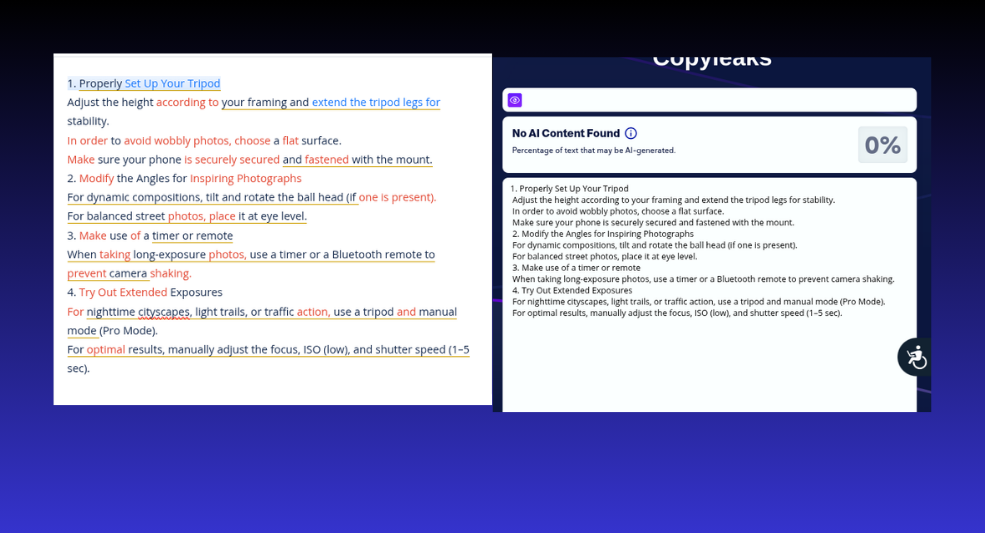
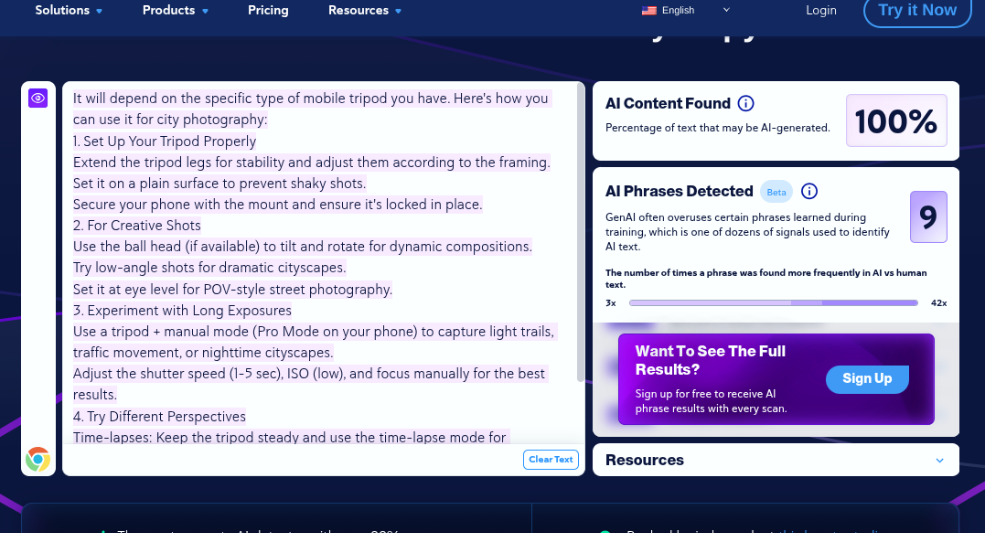
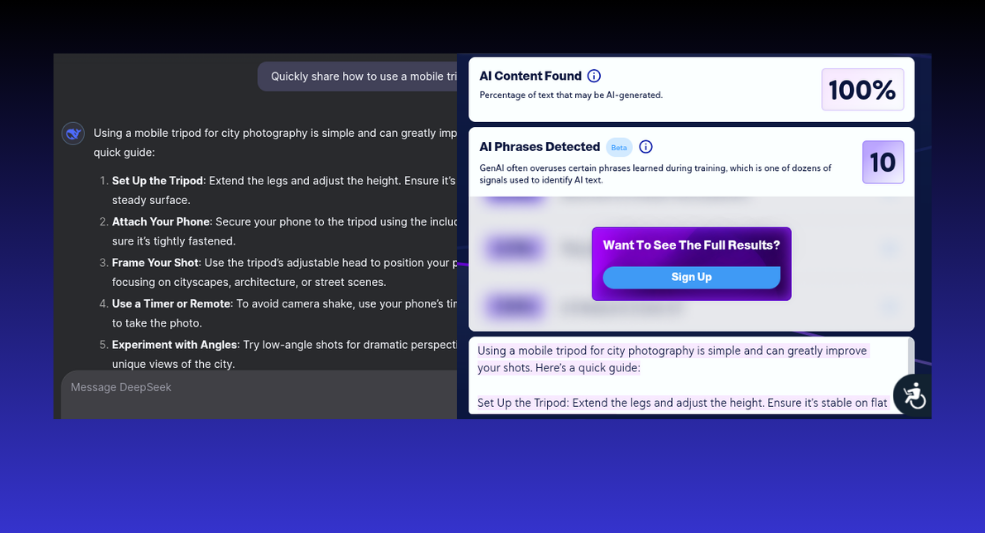
Assessment 3.3
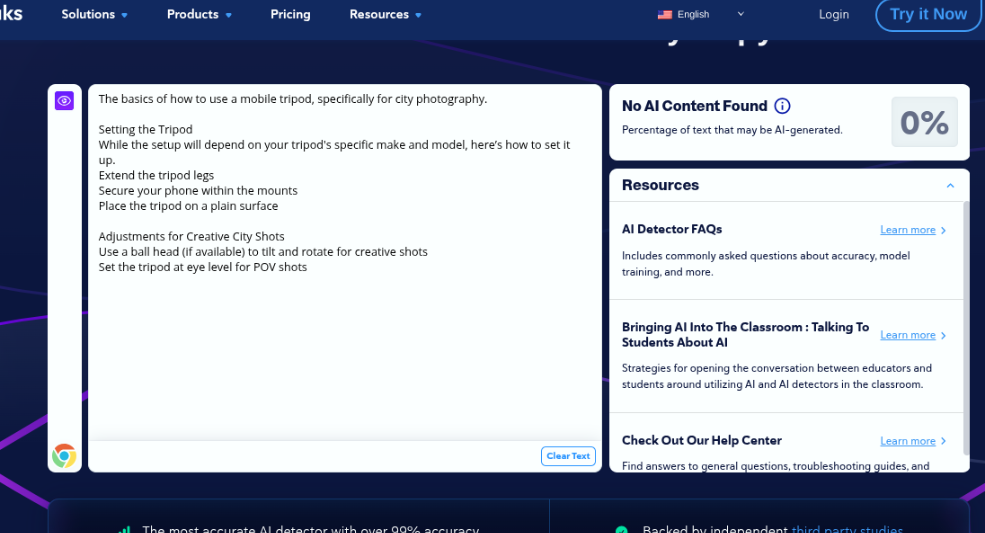
A basic guide on how to use a mobile tripod for city photography.

Assessment 3.3 Results – Pass
Once again, CopyLeaks accurately detected human-generated content.
Assessment 3 Overall Results
Out of 3 human-written texts, CopyLeaks detected two of them accurately and gave just one false positive.
CopyLeaks Accuracy Rate for Human-written Content: 66.6%
DeepSeek vs CopyLeaks
All the AI content above was sourced from ChatGPT. But how well does CopyLeaks fair against DeepSeek’s AI content?
Verdict: CopyLeaks in 2025
The latest version of CopyLeaks has certainly brought improvements, and it is far more accurate than ZeroGPT. However, it still flags content inaccurately. Combined with limited usage (even with paid plans), it isn’t the best option.
Ultimately, our verdict remains the same, i.e., it is a valuable tool for AI content detection (at 53% accuracy); however, one must be vigilant while using CopyLeaks, and it certainly needs more refinement.
Potential Consequences of CopyLeaks’ Unreliability for a Brand/Agency
Reputation Damage:
Misclassifications by CopyLeaks can lead to the unintentional publication of plagiarized or erroneous content, damaging a brand’s reputation and credibility.
Legal Risks:
False positives or negatives may expose brands/agencies to legal risks related to copyright infringement or plagiarism accusations.
Content Quality:
Inaccurate results can compromise the quality of published content, negatively impacting the audience’s trust and engagement.
Resource Wastage:
Misclassifications can lead to wasted time and resources spent on content revisions, edits, or legal disputes.
Competitive Edge:
Brands/agencies may lose their competitive edge if CopyLeaks fails to detect content misuse by competitors, affecting market positioning.
Operational Efficiency:
Reliance on an unreliable tool can hinder operational efficiency and content workflow management.
Client Trust:
Legal actions, content revisions, or reputation repair efforts can incur significant financial costs.
Financial Costs:
Legal actions, content revisions, or reputation repair efforts can incur significant financial costs.
Strategic Impact:
Brands/agencies may need to reevaluate their content strategies and compliance measures in response to CopyLeaks’ unreliability.
Continual Vigilance:
It becomes necessary to remain vigilant and consider additional content review mechanisms to mitigate the potential consequences of CopyLeaks’ limitations.
Conclusion
In our thorough evaluation, it becomes evident that CopyLeaks, despite its promise, exhibits significant unreliability. From misclassifying AI-generated content as human-written to failing to detect glaring grammatical errors, the tool demonstrated inconsistencies that cast doubt on its accuracy and effectiveness.
- Daily Limit: CopyLeaks imposes daily usage limits on its free and paid plans, which can restrict users with high-volume content analysis needs.
- Costly Premium Plans: The premium plans can be relatively expensive for individuals or small businesses, making it less accessible to those with budget constraints.
- Language Support: It may not offer as extensive language support as some other plagiarism detection tools, potentially limiting its utility for non-English content.
- False Positives: Like many plagiarism detection tools, CopyLeaks can occasionally generate false positives, flagging content as potentially plagiarized when it is not.
- Limited Integration: It may not seamlessly integrate with all content management systems, requiring additional effort for users to incorporate it into their workflow.
- Privacy Concerns: Users may have concerns about data privacy when using a cloud-based service like CopyLeaks, especially for sensitive or confidential documents.
- Limited File Types: It may have restrictions on the types of files it can analyze, potentially requiring users to convert certain formats before analysis.
These findings underscore the importance of user vigilance and supplementary manual review when utilizing CopyLeaks for content analysis. While it can be a valuable tool in the content detection landscape, our assessment highlights the need for caution and an understanding of its limitations.
Ultimately, our experiments have illuminated the unreliability of CopyLeaks, emphasizing the need for continual improvement in the realm of content analysis tools.
